Revolutionizing Structural Oversight: The Pioneering Paradigm of Next-Generation Building Inspection Systems
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving real estate and construction industries, the demand for efficient, reliable, and comprehensive building inspection processes is more critical than ever. Building inspection system plays a pivotal role in addressing this demand, offering a streamlined approach to managing inspections, ensuring compliance, and improving overall safety and quality in construction projects. This article delves into the intricacies of building inspection system software, exploring its functionalities, benefits, and the latest trends shaping its development.
Transforming Structural Safety: The Modern Building Inspection System
Building inspection system software is a specialized tool designed to assist professionals in conducting, managing, and documenting inspections of buildings and construction sites. This software automates various aspects of the inspection process, including scheduling, reporting, and compliance tracking, to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and transparency.
Core Features and Functionalities
1. Inspection Scheduling and Management:
– Automated Scheduling: Allows inspectors to schedule inspections based on predefined criteria, reducing the risk of missed or overlapping appointments.
– Calendar Integration: Syncs with calendars and scheduling tools to ensure that inspection dates and times are well-coordinated with other project activities.
2. Mobile Access and Data Collection:
– Mobile Applications: Inspectors can use mobile apps to collect data on-site, including taking photos, recording notes, and filling out checklists. This capability ensures that data is captured in real-time and is readily available for analysis.
– Offline Functionality: Enables inspections to continue even without internet connectivity, with data syncing automatically once the connection is restored.
3. Customizable Checklists and Templates:
– Predefined Templates: Offers a range of standard inspection templates that can be customized to fit specific types of inspections, such as residential, commercial, or industrial buildings.
– Checklists: Allows inspectors to create and modify checklists according to the unique requirements of each inspection, ensuring thorough coverage of all necessary components.
4. Reporting and Documentation:
– Automated Report Generation: Produces detailed inspection reports with minimal manual input, including summaries, findings, and recommendations. Reports can often be exported in various formats such as PDF or Word.
– Photo and Video Integration: Embeds multimedia files into reports to provide visual evidence of inspection findings.
5. Compliance and Regulation Tracking:
– Regulatory Compliance: Tracks compliance with local building codes, safety regulations, and industry standards, helping to ensure that all inspections meet legal requirements.
– Audit Trails: Maintains a record of all inspection activities, including changes and updates, for accountability and transparency.
6. Data Analysis and Insights:
– Trend Analysis: Analyzes inspection data to identify recurring issues or trends, which can inform preventive measures and improve overall building quality.
– Performance Metrics: Provides insights into inspector performance, inspection times, and other key metrics to optimize the inspection process.
Benefits of Building Inspection System Software
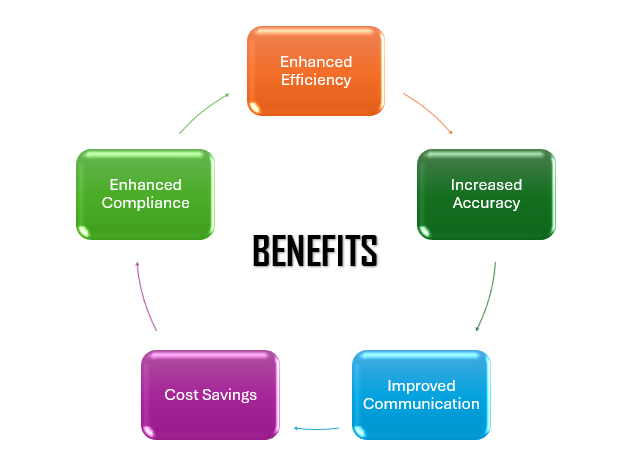
- Enhanced Efficiency:
– Automation and streamlined processes reduce the time required for scheduling, data collection, and report generation, allowing inspectors to focus on critical tasks.
- Increased Accuracy:
– Minimizes human error by providing standardized checklists, automated data entry, and real-time data collection, resulting in more reliable inspection outcomes.
- Improved Communication:
– Facilitates better communication between inspectors, project managers, and stakeholders by providing centralized access to inspection data and reports.
- Cost Savings:
reduces operational costs associated with paper-based processes, manual data entry, and inefficient scheduling, leading to overall cost savings for inspection firms and construction companies.
- Enhanced Compliance:
– Ensures adherence to building codes and regulations through automated compliance tracking and documentation, reducing the risk of legal issues and penalties.
Integrate with other systems to provide real time insights:
1. Integration with Building Information Modelling (BIM):
– The integration of building inspection software with BIM systems allows for more accurate inspections by providing detailed digital models of the building, which can be used to verify compliance with design specifications.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
– AI and machine learning technologies are increasingly being incorporated to analyze inspection data, predict potential issues, and automate certain aspects of the inspection process, enhancing overall efficiency and effectiveness.
3. Cloud-Based Solutions:
– Cloud-based inspection software provides greater accessibility, scalability, and collaboration capabilities, allowing teams to access inspection data and reports from anywhere, at any time.
4. Internet of Things (IoT):
– IoT sensors and devices can be used in conjunction with inspection software to monitor building conditions in real-time, providing additional data and insights for more comprehensive inspections.
The Inspector’s Precision Tools: Modern Essentials for Building Evaluation
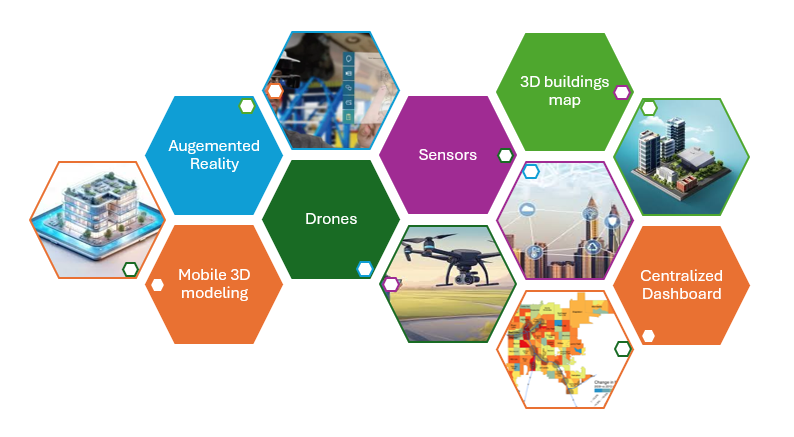
High-Tech Inspection Tools:
- A sleek, modern tablet or smartphone displaying a detailed 3D building model or inspection report, with digital overlays showing inspection data.
Drones in Action:
- A drone flying over a construction site or building, capturing images or videos, illustrating the use of advanced technology in inspections.
Augmented Reality (AR) in Use:
- An inspector wearing AR glasses or a headset, interacting with a digital overlay of building plans or structural elements.
Smart Building Sensors:
- Close-up of advanced sensors and IoT devices installed in a building, with data flowing into a central system, highlighting smart building technology.
3D Building Models:
- A computer-generated 3D model of a building or construction site, with visual indicators of inspection areas and data points.
Inspection Data Dashboard:
- A visually appealing dashboard on a computer screen showing real-time inspection data, charts, and analytics.
Conclusion
Building inspection system software has revolutionized the way inspections are conducted, offering a range of functionalities that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and compliance. As technology continues to advance, these systems will likely become even more integrated and intelligent, further improving the inspection process and contributing to safer, higher-quality buildings. For professionals in the construction and real estate industries, embracing these technological advancements is essential for staying competitive and meeting the ever-evolving demands of the industry.
